Circuit Breaker Faliure / Local Breaker Backup
50Z / 50BF / LBB /
CBF
Ha..! Ha..! Don't get confused upon reading the title. The explanation
is just here..!
This is another level of protection given for particular circuit
breakers. Each power system equipment like transformer, generator, transmission
line, etc. have its own protection relay which assures its smooth working and
safety. When a
fault occurs, one or more protection devices will operate and issue a trip
command to the relevant circuit breakers. Operation of the circuit breaker is
essential to isolate the fault and prevent, or at least limit, damage to the
power system. For transmission and sub-transmission systems, slow fault
clearance can also threaten system stability. But most of the time the
circuit breaker works fine, but due to some external fault on the circuit
breaker such as trip circuit lose contact, delayed circuit breaker operation,
circuit breaker’s internal mechanism issue, etc. it fails to trip for the
command of different relays.
Here
comes the need of a breaker failure feature in the power system. Circuit Breaker Failure
protection (CBF) monitors the circuit breaker and establishes whether it has
opened within a reasonable time. If the fault current has not been interrupted
following a set time delay from circuit breaker trip initiation, the CBF
protection will operate, whereby the upstream circuit breakers are back-tripped
to ensure that the fault is isolated.
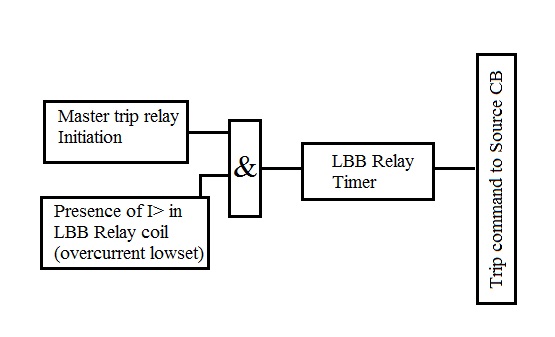
Fig 1: Logic diagram explaining the Local
Breaker Backup (LBB) Protection
All the relay having this function will
have the same logic, where there will a minimum setting of current value to
ensure there is a fault still exists even after issuing a trip command. I> value will be set to 20%
(minimum) and the timer will be set to a minimum of 200 milliseconds to ensure
safe tripping time for the actual circuit breaker. Immediately after getting an
initiation from the master trip relay, LBB Relay again sends a trip signal to
the same trip coil instantaneously and then waits for the logic to proceed. If
fault still persist and timer knocks 200 milliseconds, then LBB Relay issue trip
command to the upstream CB(s) as per the number of connected sources.
Fig 2: LBB Relay connection and trip
commands
A simple diagram to represent the logic is
given in Fig 2. Consider the fault occurred in the LV Bus and the LV Over
current Relay senses the fault first and initiates trip command to LV CB. It also initiates the LBB relay.
Since the same CT is routed through the LBB relay, fault is also sensed by it
and a counter is started since it got the initiation. It have two types of
output contacts, Delayed contact and
Instantaneous contact. When it meets
the set value, instantly a trip command is given to the same CB and wait for
the counter to reach the set value. Even at that time the fault is not cleared,
trip command is issued to the HV CB,
thus disconnecting the source from the power system where fault occurred.
50 / 50BF / LBB / CBF are all known as the
breaker failure protection. In each panel you can witness different notations from
the above give.
I hope you had a good clear idea about
what Breaker backup protection is. Some examples of LBB Relays are JVS JRC154 and almost every numerical relay have a build in function for this.
Thank you!



Comments
Post a Comment